题目连接:https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/8a19cbe657394eeaac2f6ea9b0f6fcf6
题目大意:给定二叉树的先序遍历和中序遍历结果,建立这棵二叉树。输入保证二叉树无重复结点。
思路
首先回顾一下先序遍历和中序遍历。
先序遍历是先访问左子树,再访问当前结点,最后访问右子树。
中序遍历是先访问左子树,再访问右子树,最后访问当前结点。
由于题目保证要建立的二叉树不存在重复结点,我们就可以利用先序遍历和中序遍历的特点来建立二叉树。
以先序{1, 2, 4, 7, 3, 5, 6, 8}和中序{4, 7, 2, 1, 5, 3, 8, 6}为例,显然整棵树的根结点一定是先序遍历的第一个,即1。
在中序序列中把1找到,1左边的4,7,2就是左子树,1右边的5,3,8,6就是右子树。

再来观察左子树{2,4,7}/{4,7,2},同样先序序列的第一个结点即为左子树的根结点,即2。
在中序序列中找到2,2左边的{4,7}就是它的左子树,2已经是中序序列的最后一个,它没有右子树。

再来看{4,7}/{4,7}这棵子树,这棵子树只有两个结点,并且先序和中序遍历的顺序是一样的,显然4是根结点,7是右子树的叶结点。反之,假如为{4,7}/{7,4},则4为根结点,7为左叶结点。
至此已经得到了整棵树的左半边:
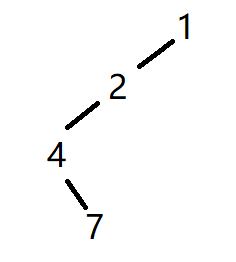
回头看1的右子树{3,5,6,8}/{5,3,8,6},显然在这棵子树中3是根结点,{5}/{5}是它的左子树,{6,8}/{8,6}是它的右子树。

在左子树{5}/{5}中只有一个结点。
在右子树{6,8}/{8,6}中,显然先序遍历和中序变量的顺序不一样,易知6是根结点,8是右叶结点。
现在整棵树都得到了:
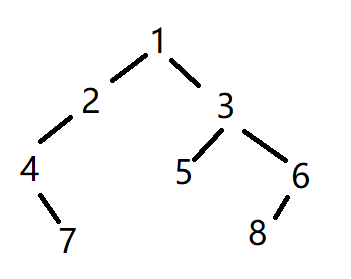
不难发现上面这个分析过程是递归分治的,根据这个思路就可以写出递归题解。
代码
import java.util.LinkedList;import java.util.Queue;/** * @author yuan * @version 0.1 * @date 2019/6/4 */public class RebuildBinaryTree { private class TreeNode { int val; TreeNode left; TreeNode right; TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } } private int[] preorder; private int[] inorder; /** * 递归方法。根据先序和中序遍历序列构建子树。 * * @param preorderStart 子树在先序遍历序列中的第一个结点所在下标 * @param inorderStart 子树在中序遍历序列中的第一个结点所在下标 * @param num 子树结点数目 * @return 子树根结点 */ private TreeNode reConstructBinaryTree(int preorderStart, int inorderStart, int num) { TreeNode root = null; if (inorderStart >= inorder.length || preorderStart < 0) { return root; } if (num == 1) { root = new TreeNode(preorder[preorderStart]); return root; } else if (num == 2) { root = new TreeNode(preorder[preorderStart]); // 先序和中序一样则应为根+右子结点,否则为根+左子结点 if (preorder[preorderStart] == inorder[inorderStart]) { root.right = new TreeNode(preorder[preorderStart + 1]); } else { root.left = new TreeNode(preorder[preorderStart + 1]); } return root; } TreeNode left = null; TreeNode right = null; // 根结点必为先序第一个,据此查找根结点在中序中的位置 for (int i = inorderStart; i < inorderStart + num; i++) { if (inorder[i] == preorder[preorderStart]) { // i大于inorderStart说明左子树存在,左子树先序从preorderStart+1开始,左子树中序从inorderStart开始,左子树结点数目为i-inorderStart if (i > inorderStart) { left = reConstructBinaryTree(preorderStart + 1, inorderStart, i - inorderStart); } // i小于inorderStart+num-1说明右子树存在,右子树先序从preorderStart+(i-inorderStart)+1开始,右子树中序从i+1开始,右子树结点数目为num-(i-inorderStart)-1 if (i < inorderStart + num - 1) { right = reConstructBinaryTree(preorderStart + i - inorderStart + 1, i + 1, num - i + inorderStart - 1); } root = new TreeNode(preorder[preorderStart]); root.left = left; root.right = right; break; } } return root; } public TreeNode reConstructBinaryTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) { this.preorder = preorder; this.inorder = inorder; return reConstructBinaryTree(0, 0, preorder.length); } /** * 测试用,BFS打印 * * @param root 根结点 */ public void printTree(TreeNode root) { Queue queue = new LinkedList<>(); queue.offer(root); StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder(); result.append(root.val); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { TreeNode node = queue.poll(); if (node.left == null && node.right == null) { continue; } if (node.left != null) { queue.offer(node.left); result.append(",").append(node.left.val); } else { result.append(",#"); } if (node.right != null) { queue.offer(node.right); result.append(",").append(node.right.val); } else { result.append(",#"); } } System.out.println(result.toString()); } public static void main(String[] args) {// int[] preorder = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7};// int[] inorder = {3, 2, 4, 1, 6, 5, 7};// int[] preorder = {1, 2, 4, 3, 5, 6};// int[] inorder = {4, 2, 1, 5, 3, 6}; int[] preorder = {1, 2, 4, 7, 3, 5, 6, 8}; int[] inorder = {4, 7, 2, 1, 5, 3, 8, 6}; RebuildBinaryTree solution = new RebuildBinaryTree(); solution.printTree(solution.reConstructBinaryTree(preorder, inorder)); }}
附牛客网评论区最高赞代码,写法更加简洁
public TreeNode reConstructBinaryTree(int [] pre,int [] in) { TreeNode root=reConstructBinaryTree(pre,0,pre.length-1,in,0,in.length-1); return root;}private TreeNode reConstructBinaryTree(int [] pre,int startPre,int endPre,int [] in,int startIn,int endIn) { if(startPre>endPre||startIn>endIn) return null; TreeNode root=new TreeNode(pre[startPre]); for(int i=startIn;i<=endIn;i++) if(in[i]==pre[startPre]){ root.left=reConstructBinaryTree(pre,startPre+1,startPre+i-startIn,in,startIn,i-1); root.right=reConstructBinaryTree(pre,i-startIn+startPre+1,endPre,in,i+1,endIn); break; } return root;}